| MadSci Network: Biochemistry |
Hi Amber,
The enzyme catalase carries out the following reaction:
H2O2 + H2O2 -> 2 H2O + O2.. or it takes two molecules of hydrogen peroxide and converts them to two water molecules plus a molecule of oxygen gas. A common test for the presence of catalase in bacteria involves suspending a sample of the microbes in a dilute solution of hydrogen peroxide. If the organisms produce catalase, bubbles form in the solution from the release of oxygen.
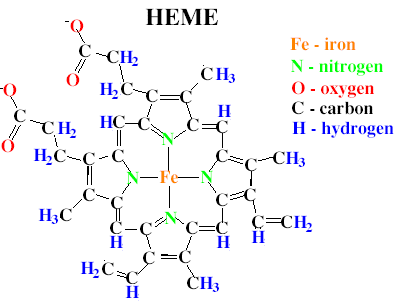
An answer of 'how' catalase carries out this reaction is a bit more complicated, and enters the relm of organic chemistry, thermodynamics and enzyme kinetics. I presume you haven't had any of these topics in your science class, so I'll try to keep it simple! As with all enzymes, catalase is a protein, meaning that it is synthesized within the cell from building blocks called amino acids (kind of like pieces from a complicated leggo set..). In addition to the amino acids that make up the protein, catalase carries around a heme group. You may have heard of heme before, particularly as hemoglobin - the stuff that makes your blood red. In the middle of the heme group sits an iron atom (see the picture below). The catalase enzyme uses this iron atom to help it break the bonds in the two molecules of hydrogen peroxide, shifting the atoms around to release two molecules of water and a molecule of oxygen gas.
-L.B.

Try the links in the MadSci Library for more information on Biochemistry.