| MadSci Network: Botany |
Dear Jeremy,
Good question! First, let's have a look at what's in aspirin and tylenol tablets, the sort of stuff you'd normally take for a headache. The chemical in aspirin which sorts your headache out is called acetylsalicylic acid. The chemical in tylenol is called acetaminophen (also known as paracetamol). Lets look at these individually:
Acetaminophen/paracetamol (tylenol): When acetaminophen was first invented it was made artificially from other chemicals. We don't really understand entirely why it works (although a lot of scientists are currently trying to find out!). We don't really know would happen if we fed it to a plant. Plants obviously don't get headaches, so we're not helping here. What we do know about acetaminophen suggests that it probably won't do a lot in plants. It might be toxic in large amounts (as it is in humans), but I'm not really sure how much it would take to harm a plant!
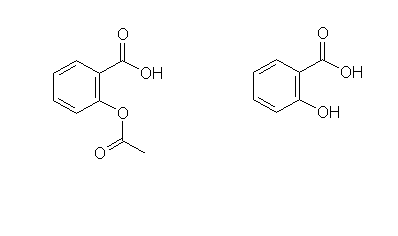
Acetysalicylic acid (aspirin): A long time ago people used to use bark from the willow tree as a painkiller. It contains salicylic acid. Scientists found a way to make a very similar chemical called acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) which works in exactly the same way. We now use acetysalicylic acid as aspirin. The two chemicals look very similar (see below);

It turns out that plants use salicylic acid to let parts of the plant know if other bits of it are being damaged or attacked. This is a really clever trick to keep the plant healthy. If a fungus starts eating the bottom leaves of the plant, those leaves make salicylic acid, which is sent through the stem up to the rest of plant. The rest of the leaves notice this message, and start building defences. They start producing all kind of nasty chemicals to stop the fungus eating them too. This protects the rest of the plant.
You can use aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) to fool the plant into switching on its defenses. When you water a plant with aspirin dissolved in water, the acetysalicylic acid is taken up by the roots. It looks enough like salicylic acid to fool the plant, and it switches on its defenses.
The response is pretty sensitive - too much aspirin will kill the plant. People often use it to keep cut roses healthy - putting a quarter of a tablet in about half a litre of water should work.
Myself and the many other scientists are trying to find out how we can use this trick to keep our crop plants healthy. Imagine how helpful it would be if we could simply water our crops with aspirin, and make them resistant to fungi, bugs and viruses! We've found the response works against viruses, bacteria and fungi. At the moment we're trying to find out how it works, and if we can use it on crop plants.
Don't forget - the effects in plants are very different to those in people - you can't make yourself resistant to bugs by taking aspirin!
Hope this helps.
All the best, Carl
Try the links in the MadSci Library for more information on Botany.