| MadSci Network: Physics |
An interesting question. If we assume that the air surrounding the bottle is still (as opposed to the wind blowing), the water molecules will evaporate from the surface of the water and diffuse through the air in the bottle until it escapes from the opening. We also need to assume that the rate limiting step isn't evaporation from the surface of the water, and that the water concentration in the air surrounding the bottle is lower than the concentration within the bottle.
The diffusion of gas molecules is subject to "Fick's laws", relationships derived by Adolf Fick in the year 1855.
The general equation for Fick's First Law of Diffusion is
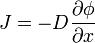
J=-D* d phi/d x
where
* J is the diffusion flux in dimensions of [(amount of substance) length−2 time−1]. J measures the amount of substance that will flow through a small area during a small time interval.
* \, D is the diffusion coefficient or diffusivity in dimensions of [length2 time−1]
* \, \phi (for ideal mixtures) is the concentration in dimensions of [(amount of substance) length−3], example (\tfrac\mathrm{mol}{\mathrm m^3})
* \, x is the position [length].
In this animated gif, the diffusion away from a surface is illustrated:
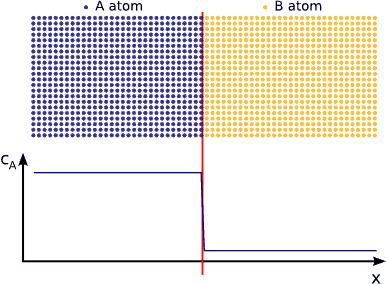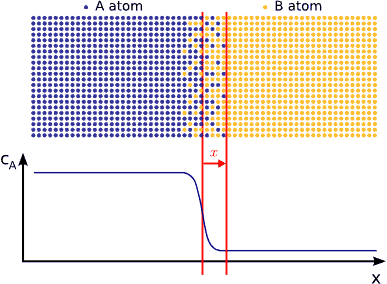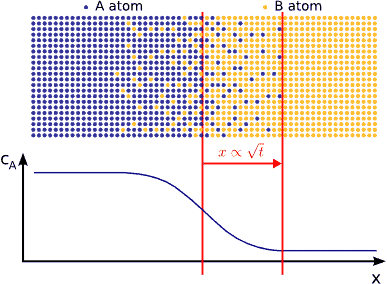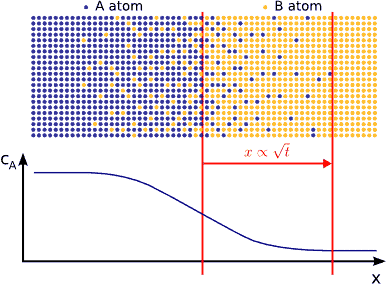
The important part of this image is to observe that the rate that the evaporated atoms move away from the surface will be controlled by the distance they have to travel, as well as the area available for them to diffuse through.
Put another way, it will take more time for molecules to diffuse through a small hole in a bottle than through a large hole. Likewise it will be less difficult for molecules to diffuse through a short hole than through, for example, a long straw. The more area that is available for diffusion, and the shorter distance that molecules have to diffuse, the faster they will diffuse.
Simply put, water will evaporate from a bottle with a wide, short neck than from a bottle with a long, narrow neck.
Try the links in the MadSci Library for more information on Physics.